Soilless gardening has gained immense popularity, and for good reason. Systems like hydroponics and aquaponics allow you to grow fresh, healthy plants using significantly less water, less space, and far more control than traditional soil gardening. But while these two methods are often mentioned together, they are not the same, and choosing the wrong one can lead to frustration, unnecessary expenses, and stalled progress.
At first glance, aquaponics and hydroponics may seem nearly identical. Both grow plants without soil. Both rely on water, pumps, and controlled environments. And both are capable of producing impressive yields. However, what happens inside each system, and what’s required to keep it running successfully, differs in ways that matter.
Hydroponics depends on synthetic nutrient solutions mixed by the grower to feed plants directly. Aquaponics, on the other hand, relies on a living ecosystem, where fish, beneficial bacteria, and plants work together to supply nutrients naturally. That single difference impacts everything from ongoing costs and maintenance to sustainability, learning curve, and long-term success.
This blog will walk you through:
- How hydroponics and aquaponics actually work
- The real differences in cost, maintenance, and effort
- Which system is better suited for beginners and long-term growers
- How to choose the right system before you invest time and money
If you’re exploring soilless gardening and want a solution that aligns with your goals, whether that’s sustainability, simplicity, or long-term savings, you’re in the right place.

What Is Aquaponics? How Fish, Plants, and Bacteria Work Together
Aquaponics is a food-growing system that combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (growing plants in water). Instead of relying on synthetic nutrient solutions, aquaponics uses a natural, self-sustaining ecosystem where fish, beneficial bacteria, and plants support one another.
In aquaponics, fish produce waste, and the beneficial bacteria convert that waste into plant-available nutrients, and plants absorb those nutrients, cleaning the water before it returns to the fish. Once balanced, the system largely maintains itself with minimal outside inputs.
How Aquaponics Systems Work
Every aquaponics system depends on three living components:
- Fish, which produce nutrient-rich waste
- Beneficial bacteria, which convert ammonia into nitrates
- Plants, which absorb nutrients and purify the water
This process is known as the nitrogen cycle, and it’s the foundation of a successful aquaponics system. Rather than mixing nutrients by hand, the grower focuses on maintaining healthy fish, stable water conditions, and proper system flow.
The Role of Beneficial Bacteria
Beneficial bacteria are what make aquaponics possible. These naturally occurring microbes:
- Convert toxic ammonia into nitrites and then nitrates
- Create a steady, plant-friendly nutrient supply
- Help stabilize water chemistry over time
Once established, bacterial colonies continue working around the clock, reducing the need for constant adjustments.
Why Many Growers Choose Aquaponics
Aquaponics appeals to growers who want:
- A more sustainable growing method
- Fewer recurring input costs
- Less dependence on synthetic nutrients
- A system that becomes more stable with time
While aquaponics does involve caring for fish, many growers find this easier than constantly measuring and adjusting nutrient solutions. The system itself provides feedback, healthy fish and vibrant plants are signs everything is in balance.
Components of an Aquaponics System
1. Fish Tank:
The fish tank is the central component where fish are raised. The size and type of fish tank can vary based on the scale of the aquaponics system and the species of fish being raised.
2. Grow Beds:
The containers where plants are grown. Grow beds are typically filled with a grow media like gravel, clay pellets, or lava rock, which support plant roots and facilitate water drainage and aeration.
3. Water Circulation System:
A network of pumps and pipes that ensures the continuous movement of water from the fish tank to the grow beds and back. This system maintains water flow and ensures that plants receive nutrients and fish have clean water.
4. Biofilter and Bacteria Role:
A crucial component that houses beneficial bacteria. These bacteria convert toxic ammonia from fish waste into nitrites and then into nitrates, which are less harmful and can be absorbed by plants as nutrients. This biological filtration process is essential for maintaining water quality and ensuring the health of both fish and plants.
Challenges and Limitations of Aquaponics
1. Initial Setup Costs: Setting up an aquaponics system can be expensive. It involves building fish tanks grow beds, and installing pumps and aeration systems. However, long-term savings in water and fertilizer costs can offset these initial expenses.
2. Maintenance and Monitoring: Aquaponics systems require consistent monitoring of water quality, fish health, and plant growth. Maintaining the balance between fish, bacteria, and plants can be challenging.
3. Limited Crop Variety: Aquaponics can grow a wide range of crops, but certain plants may not thrive in this system due to specific nutrient requirements or space constraints. It's essential to choose crops that are well-suited to aquaponics.
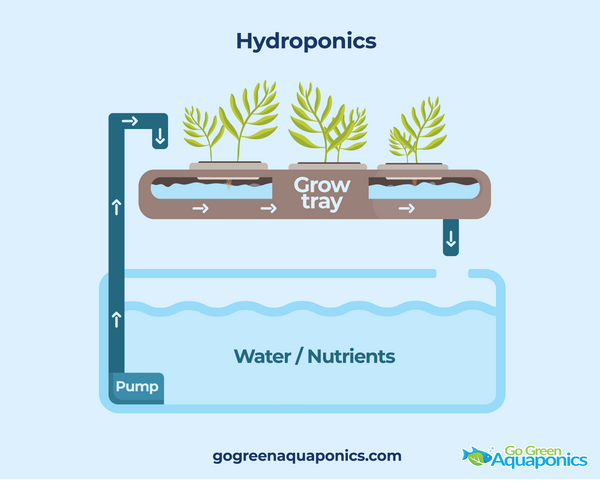
What Is Hydroponics? How It Works and When It Makes Sense
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil by delivering nutrients directly to the plant roots through water. Instead of pulling minerals from soil, plants receive a carefully mixed nutrient solution that contains everything they need to grow, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and trace minerals.
In a hydroponic system, the grower is responsible for creating and maintaining this nutrient solution. Water, nutrients, oxygen, and light must all be carefully balanced to keep plants healthy. When done correctly, hydroponics can produce fast growth and impressive yields, which is why it’s commonly used in commercial greenhouses and controlled indoor environments.
How Hydroponic Systems Work
Most hydroponic setups include:
- A water reservoir holding a nutrient-rich solution
- A pump or air stone to oxygenate the water
- Plant supports such as net pots or grow channels
- A method for delivering nutrients to plant roots
The nutrients are dissolved directly into the water, and plants absorb them immediately. Because there’s no soil to buffer mistakes, nutrient levels must be monitored closely to avoid deficiencies or nutrient burn.
Common Types of Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponics isn’t a single system, it’s a category that includes several designs, such as:
- Deep Water Culture (DWC):Plant roots sit directly in oxygenated nutrient water
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT):A thin stream of nutrients flows over plant roots
- Drip Systems: Nutrients drip onto roots at controlled intervals
Each system has its strengths, but all rely on consistent nutrient management.
When Hydroponics Makes Sense
Hydroponics is often a good fit if you:
- Want maximum control over nutrients
- Are comfortable measuring and adjusting water chemistry
- Plan to grow primarily leafy greens or herbs
- Don’t mind purchasing and mixing nutrient solutions regularly
For growers who enjoy hands-on control and precision, hydroponics can be a powerful growing method.
That said, hydroponics also requires ongoing attention. Nutrient solutions must be replaced, pH must be adjusted, and mistakes can show up quickly in plant health. For some growers, this level of control is exciting. For others, it becomes time-consuming over the long run.
Components of a Hydroponics System
1. Water Reservoir: A container that holds the nutrient solution. The size of the reservoir depends on the scale of the hydroponic system. It serves as the central source of water and nutrients for the plants.
2. Grow Medium: While hydroponics is a soil-less method, plants often need support, which is provided by inert grow media. Common grow media include rockwool, clay pellets, perlite, vermiculite, and coconut coir. These materials help anchor the plants, provide aeration, and retain moisture.
3. Nutrient Solution: A carefully balanced mixture of water and essential minerals that plants need for growth. This solution typically contains macronutrients (such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) and micronutrients (such as iron, magnesium, calcium) tailored to the plants’ requirements.
4. Pump and Irrigation System: A system of pumps and tubing that delivers the nutrient solution to the plant roots. Depending on the type of hydroponic system, this may involve continuous or intermittent pumping to ensure plants receive adequate nutrients and oxygen.
Challenges and Limitations of Hydroponics
- Reliance on Artificial Nutrients: Hydroponic systems rely on synthetic nutrient solutions, which can be expensive and raise concerns about sustainability and environmental impact.
- Vulnerability to System Failures: Hydroponic systems depend on mechanical components like pumps and timers. Failures in these components can lead to disruptions in nutrient delivery, potentially harming crops.
- Environmental Concerns: Disposal of used nutrient solutions can be problematic, as they may contain excess nutrients that can harm local ecosystems if not appropriately managed.

Aquaponics vs Hydroponics: Key Differences at a Glance
While aquaponics and hydroponics share similarities on the surface, the way they deliver nutrients, manage water, and function long-term is fundamentally different. Understanding these differences helps you choose a system that fits not just your space, but your lifestyle, budget, and goals.
1. Nutrient Source:
- Hydroponics:Nutrients are manually mixed using synthetic or mineral-based solutions. The grower must monitor concentration and replace the solution regularly.
- Aquaponics: Nutrients are produced naturally from fish waste and converted by beneficial bacteria into plant-available nitrates.
2. Water Usage:
- Hydroponics:Uses less water than soil gardening, but still requires periodic draining and replacement of nutrient solutions.
- Aquaponics: Recirculates water continuously, with plants cleaning the water before it returns to the fish.
3. Ongoing Costs:
- Hydroponics: Requires ongoing purchases of nutrient solutions, pH adjusters, and supplements.
- Aquaponics: Primary recurring cost is fish feed, which is typically less expensive and used more efficiently.
4. Maintenance and Monitoring:
- Hydroponics:Requires frequent monitoring of pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and nutrient strength.
- Aquaponics:Focuses on observing fish health, water clarity, and system balance rather than constant chemical testing.
5. Sustainability & Environmental Impact:
- Hydroponics:Efficient but dependent on manufactured nutrients.
- Aquaponics: Produces both plants and fish in a closed-loop ecosystem with minimal waste.
6. Learning Curve:
- Hydroponics: Easier to start quickly, but mistakes can show up fast.
-
Aquaponics: Takes time to establish bacteria but becomes more forgiving and stable over time.

Factors to Consider in Choosing the Right System for You
In choosing whether aquaponics or hydroponics depends on your specific goals, resources and preferences. Here are some factors to consider in helping you decide which system is suitable for your needs.
1. Space and Resources
A. Aquaponics:
- Aquaponics systems typically require more space due to the need for fish tanks and grow beds.
- Ideal for: Large backyards, greenhouses, or dedicated indoor spaces where you can control environmental conditions.
B. Hydroponics:
- Hydroponics systems are generally more compact and can be adapted to various spaces, including small apartments, balconies, or vertical gardens.
- Ideal for: Limited spaces, urban environments, or areas where land availability is restricted.
2. Desired Produce
A. Aquaponics:
- Aquaponics is well-suited for growing leafy greens, herbs, and some fruiting plants like tomatoes and cucumbers. The choice of fish species is also important, as they must thrive in the same conditions suitable for the plants.
- Best for: Mixed production of vegetables, herbs, and fish for a more diverse yield.
B. Hydroponics:
- Hydroponics can support a wide variety of plants, including vegetables, fruits, herbs, and flowers. If your focus is on cultivating specific plants that require tailored nutrient profiles, hydroponics offers greater flexibility.
- Best for: Specialized crop production, including off-season and exotic plants.
3. Level of Expertise and Willingness to Manage Complexity
A. Aquaponics:
- Aquaponics systems require a higher level of expertise because of the need to manage both fish and plant components.
- Suitable for: Experienced growers, hobbyists, or those willing to invest time in learning and managing a complex system.
B. Hydroponics:
- Hydroponics is simpler to set up and manage, making it more accessible for beginners. The focus is primarily on plant care, nutrient solution management, and environmental control.
- Suitable for: Beginners, hobbyists, educators, or commercial growers looking for a straightforward growing method.
4. Sustainability Goals
A. Aquaponics:
- Aquaponics is inherently sustainable due to its closed-loop system that recycles water and nutrients. It produces organic yields with no synthetic fertilizers or pesticides. If your goal is to minimize environmental impact and promote sustainable practices, aquaponics aligns well with these values.
B. Hydroponics:
- While hydroponics is more sustainable than traditional soil farming, it does rely on synthetic nutrients and can have higher energy consumption, especially with artificial lighting. However, it still offers significant water savings and the ability to produce food in areas with poor soil or limited water resources.
Conclusion: Which System is Right for You?
Both systems have its own benefits and challenges and offers innovative, and sustainable alternatives to traditional farming. Choosing between aquaponics and hydroponics depends on a careful assessment of your goals, resources, and preferences.
Aquaponics is an appealing option for those who are interested in a more holistic, integrated approach to sustainable farming. Its resource efficiency, minimal waste production, and potential for organic produce are significant advantages. However, the complexity and higher initial costs may require a greater commitment in terms of time and knowledge.
Hydroponics, on the other hand, excels in its simplicity and adaptability, with lower setup costs and a more straightforward learning curve. Its ability to produce rapid, high-density yields in controlled environments makes it ideal for those looking to maximize space and achieve faster harvests. However, the dependence on external nutrient sources and the need for precise monitoring present their own set of challenges.
Ultimately, the best system for you will depend on your specific circumstances. Whether you choose aquaponics or hydroponics, both systems offer exciting opportunities to cultivate fresh, sustainable produce and contribute to a greener future.
Ready to Take the Next Step?
If you want to start your own aquaponics system and want step-by-step visual guidance, get this beginner-friendly Aquaponics Video Guide. This in-depth, easy-to-follow video covers everything from system setup to troubleshooting, and is designed specifically for first-time growers.
👉 Click here to get access to the Aquaponics Video Guide!
Turn your knowledge into action by growing smarter today and enjoy the satisfaction of fresh, homegrown food, all from the power of a balanced, natural system.







Leave a comment (all fields required)