At the heart of aquaponics lies a meticulously designed system composed of various components working in synergy. Among these components, the sump tank plays an important role that serve as a cornerstone for efficient water management and system stability.
In this article, we will discuss the role of sump tanks in aquaponics, explore their significance, functions, design considerations, and practical implementation. Understanding the role of the sump tank is essential for unlocking the full potential of your aquaponics system.
What is a Sump Tank?
A sump tank, also known as a reservoir or collection tank, is a crucial component of an aquaponics system. Its primary function is to serve as a centralized container for holding and managing water within the system. The sump tank acts as a buffer, helping to regulate water levels, maintain system stability, and facilitate efficient water management.
It collects excess water from various components of the aquaponics system, such as grow beds and fish tanks, and provides a centralized location for filtration, nutrient supplementation, and other maintenance tasks. Additionally, the sump tank can serve as a backup reservoir in case of power outages or pump failures, which ensure the continuous operation of the system and prevent any disruptions to the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
The Role of Sump Tank in Aquaponics Systems
The sump tank is a crucial component of an aquaponics system. It serves as a reservoir for water and playing a vital role in maintaining system stability and efficiency. Essentially, the sump tank acts as a buffer which ensures a consistent water level throughout the system and providing a space for excess water to collect.
The sump tank regulates water flow, helps in nutrient distribution, and facilitates the removal of solid waste and debris, which improves the water quality and minimizing the risk of clogs and blockages in the system. It also serves as a backup in case of power outages or pump failures, which prevent the disruptions to the delicate balance of the aquaponics ecosystem.
The Ideal Location of Sump Tank in the Aquaponics System
The sump tank is typically positioned at a lower elevation than the other components of the aquaponics system, such as the fish tanks and grow beds. This position allows gravity to assist in the flow of water, with water naturally draining into the sump tank from higher points in the system.
The sump tank is often placed beneath the grow beds or fish tanks, although its exact location may vary depending on the design and layout of the system. Placing the sump tank at a strategic location ensures efficient water collection and distribution throughout the system, promoting optimal nutrient cycling and water quality.
How Sump Tanks Work?
Sump tanks operate on the principle of gravity-driven water flow and hydraulic equilibrium. As water is pumped or gravity-fed into the grow beds or fish tanks, it eventually flows back down into the sump tank because of gravity. The sump tank collects this water, which may contain fish waste, uneaten fish food, and other debris. From the sump tank, water is then pumped back into the grow beds or fish tanks, completing the cycle.
The sump tank may also house the filtration systems, such as mechanical filters or biological filters, which help remove solid waste and maintain water quality. By collecting and redistributing water, the sump tank ensures a consistent water level throughout the system, prevents flooding, and facilitates efficient nutrient cycling which promotes the health and productivity of both fish and plants in the aquaponics system.
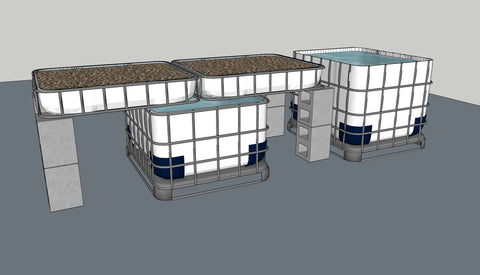
Advantages of Using a Sump Tank in Aquaponics System
1. Improved Water Management
One of the primary advantages of using sump tank in your aquaponics system is improved water management. The sump tank serves as a central reservoir for collecting and storing water from various components of the system, such as grow beds and fish tanks. This centralized water collection allows for better control and regulation of water levels throughout the system and helps prevent flooding in grow beds or fish tanks which ensures a consistent and optimal water level for plants and aquatic animals.
2. Enhanced System Stability
By providing a buffer for water storage, the sump tank helps maintain balance within the system, which prevents fluctuations in water levels and pressure. This stability is essential for the health and well-being of both fish and plants, as sudden changes in water conditions can stress or even harm aquatic organisms.
3. Increased Nutrient Availability
As water circulates through the system, it passes through the sump tank, where it may undergo filtration and nutrient supplementation. This process helps replenish essential nutrients in the water, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are vital for plant growth and development. By ensuring a constant supply of nutrients, the sump tank enhances the overall health and productivity of the plants, leading to higher yields and healthier crops.
4. Reducing Pump Stress
By collecting and storing excess water, the sump tank reduces the frequency and intensity of pump cycling, as pumps do not need to work as hard to maintain water levels in grow beds or fish tanks. This reduced pump stress not only conserves energy but also minimizes wear and tear on pump components which reduce the likelihood of pump failures and costly repairs.
5. Boosting Circulation and Oxygenation
A well-designed sump tank with the right pump can significantly improve water circulation throughout the entire system.
6. Reservoir for Emergencies
Even the most meticulously maintained aquaponics system might require occasional water top-ups during maintenance or because of evaporation. A sump tank acts as a built-in reservoir, providing readily available water to maintain optimal water levels without disrupting the delicate balance of your system
Design Considerations for Sump Tanks
1. Size and Capacity
One of the first considerations when designing your sump tank is to determine its size and capacity. The size should be proportional to the overall size of the system and the volume of water it needs to accommodate. Factors such as the number of grow beds, fish tanks, and the desired water turnover rate will influence the size requirements. It's recommended to have a sump tank large enough to hold at least 10-20% of the total system volume. This ensures sufficient water storage capacity for buffering fluctuations and provides room for any potential expansion of the system in the future.
2. Material Selection
The common materials used for sump tank are plastic, fiberglass, concrete, and metal. Plastic tanks are lightweight, affordable, and easy to install, making them a popular choice for smaller systems. Fiberglass tanks offer durability and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for larger systems or outdoor installations.
Concrete tanks are sturdy and can be custom-built to specific dimensions but may require additional waterproofing. Metal tanks, such as stainless steel or galvanized steel, are durable and resistant to corrosion but may be more expensive. When selecting a material for the sump tank, consider factors such as cost, durability, compatibility with the aquatic environment, and ease of maintenance.
3. Placement and Integration with Other Components
The placement of the sump tank within the aquaponics system is critical for optimizing water flow and system efficiency. Ideally, the sump tank should be positioned at a lower elevation than the other components, such as grow beds and fish tanks, to allow for gravity-driven water flow. Placing the sump tank centrally within the system can help facilitate even distribution of water and nutrients to all components.
4. Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance tasks may include routine inspection of the tank for leaks or damage, cleaning and removal of debris, monitoring water levels and quality parameters, and servicing of pumps and filtration systems.Periodic checks for signs of wear or deterioration in tank materials should be conducted to prevent potential issues. The frequency and extent of maintenance will depend on factors such as system size, stocking densities, and environmental conditions.

Setting Up a Sump Tank in Your Aquaponics System
1. Step-by-Step Installation Process
- Select the Sump Tank: Choose a sump tank that is appropriately sized for your aquaponics system. Consider factors such as the size of your grow beds and fish tanks, as well as the overall water volume of the system.
- Position the Sump Tank: Place the sump tank in a location that allows for easy access and efficient water flow. Ideally, the sump tank should be situated at a lower elevation than the other components of the system to facilitate gravity-driven water flow.
- Connect Plumbing: Install plumbing connections to facilitate water flow between the sump tank, grow beds, and fish tanks. Use PVC pipes and fittings to create a system of pipes that allows water to circulate smoothly throughout the system.
- Install Pumps and Valves: Install water pumps in the sump tank to facilitate the movement of water throughout the system. Use valves to control the flow of water and regulate water levels in the sump tank and other components of the system.
- Add the Filtration Systems: Integrate filtration systems into the sump tank to remove solid waste and debris from the water. Consider using mechanical filters, biological filters, or other filtration media to maintain water quality and prevent clogs in the system.
- Test for Leaks: Before filling the sump tank with water, thoroughly inspect all plumbing connections and seals for leaks. Repair any leaks as needed to ensure the integrity of the system.
- Fill the Sump Tank: Once the plumbing connections are secure, fill the sump tank with water. Ensure that the water level is sufficient to cover the pump intake to prevent air from being drawn into the pump.
- Start the System: Start the water pumps and allow the system to cycle for a few days to establish biological filtration and stabilize water parameters. Monitor water quality and make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal conditions for fish and plants.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting Tips
A. Potential Issues with Sump Tanks
- Clogging: Sump tanks can become clogged with debris or sediment, restricting water flow and causing backups in the system.
- Overflow: Without proper overflow protection, sump tanks may overflow, leading to flooding and water damage.
- Air Entrapment: Improper pump placement or insufficient water levels in the sump tank can result in air being drawn into the pump, causing cavitation and pump damage.
- Algae Growth: Excessive light exposure or nutrient buildup in the sump tank can lead to algae growth, which can clog filters and degrade water quality.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Sump tanks located outdoors or in uncontrolled environments may experience temperature fluctuations, impacting fish and plant health.
B. Troubleshooting Common Problems
- Clogged Filters: If filters become clogged, clean or replace them as needed to restore water flow and maintain water quality.
- Pump Cavitation: Check water levels in the sump tank and ensure pumps are properly submerged to prevent cavitation. Adjust pump placement if necessary.
- Overflow Issues: Inspect overflow mechanisms for blockages or malfunctions. Adjust overflow pipes or install additional overflow protection if necessary.
- Algae Growth: Control algae growth by reducing light exposure, maintaining proper nutrient levels, and implementing algae-eating organisms such as snails or algae-eating fish.
- Temperature Regulation: Use insulation or shade structures to regulate water temperature in outdoor sump tanks. Consider using heaters or chillers to maintain stable water temperatures in controlled environments.
Conclusion
Incorporating sump tank into your aquaponics system offers numerous benefits, ranging from improved water management and system stability to increased nutrient availability and reduced pump stress. With careful design considerations, proper installation, and proactive maintenance, you can harness the full potential of sump tanks to create thriving ecosystems that produce abundant yields of healthy, sustainable food.






Sagau
August 26, 2021
The explanation on the purpose of sump tank is great, simple and easy to understand. In the diagrams provided is it corect to say the grow beds act as the biofilter? I intend to DIY commercial aquaponics. Is it corect to put a separate biofilter in brtween the fish tank and the sump tank. Your advice is very much appreciated, thank you.